“In future, we would like to receive the delivery note number, the carrier and the tracking number from you in good time. We will require this information from our suppliers in future. That is why we are currently introducing a portal. The invitation will be sent to you in the next few days.”
As a sales employee, how do you deal with this “request”? The world is becoming more dynamic and the above-mentioned customer request is understandable due to uncertain supply chains. In the best case scenario, your company can implement electronic exchange via EDI. In this article, I will explain what EDI is and how it generates benefits.
Brief summary:
- “Electronic data interchange” stands for EDI and describes the electronic exchange of data between IT systems
- EDI enables the automation of business processes. Processes can be rethought, manual errors reduced, efficiency increased and process costs lowered.
- Well-known EDI standards are EDIFACT, OpenTRANS, VDA, ZUGFerd or X-Rechnung
- Messages can be exchanged via communication channels such as HTTPS, AS2 or SMTP (via e-mail)
- EDI message types such as order, order confirmation, shipping notification or invoice are often implemented in C-parts management
What is electronic data interchange via EDI?
EDI stands for electronic data interchange. This refers to the transfer of electronic data in or between IT systems. The exchange of documents or messages (e.g. orders, shipping notifications) takes place automatically without human intervention. Structured data is used in accordance with international or industry-specific standards.
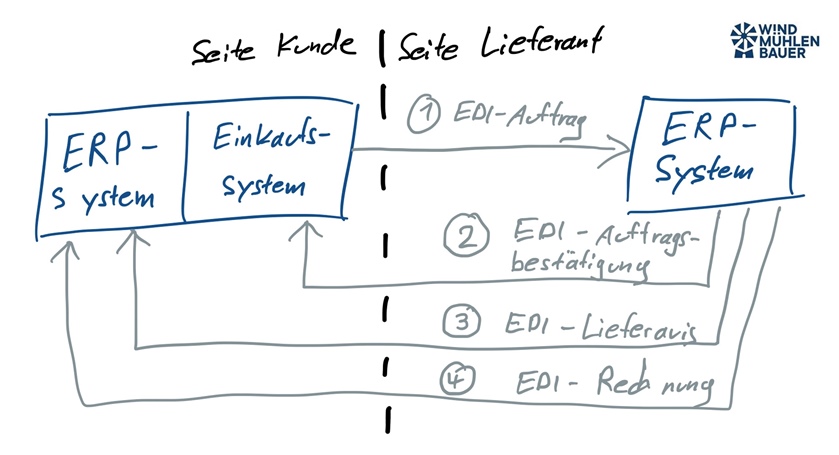
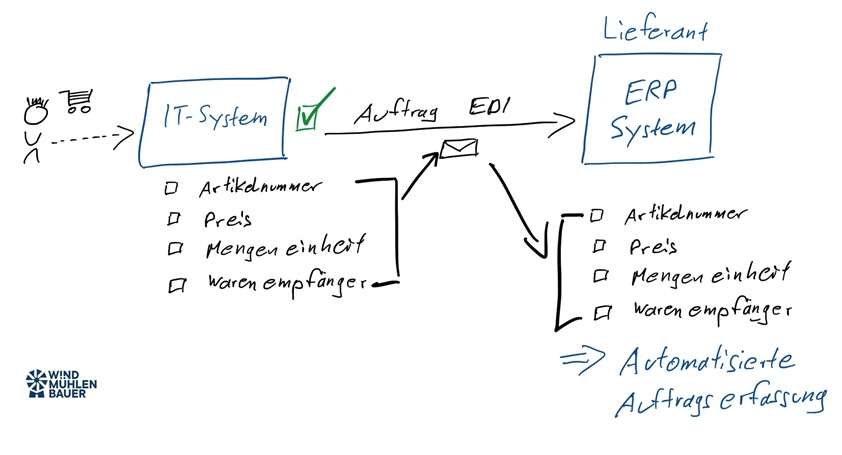
What are the benefits of using EDI?
I would like to use this example to illustrate the benefits. The customer wants to receive the delivery note number. Until now, the enclosed delivery bill has been used in goods receipt to manually enter the number in the customer’s own IT system. With the use of EDI, this is done automatically. Once the goods issue has been posted at the supplier, the shipping notification is sent to the customer system. In addition to the delivery note number, the packing dimensions and quantities of the items are stored in this. The import takes place automatically before the goods are delivered to the customer. This increases the transparency of goods receipt and saves this manual activity.
EDI therefore enables the automation of business processes. As a result, processes can be rethought, manual errors reduced, efficiency increased and process costs lowered. Process costs represent the value of working time generated by the manual activities of employees.
Advantages of EDI
- Short-term exchange of information
- Avoid repeated collection of the same information
- Avoid errors during data entry
- Automation of processes such as payment of invoice amounts without manual intervention
- Savings in process costs
- Increased efficiency
- No media disruptions
Optimized business processes through increased transparency
- Increasing the quality of information for purchase orders
- Automation of the invoicing process
- Optimization of stocks
- Optimization of incoming goods
- System-supported identification of deviations, e.g. from changed delivery dates or changed prices
➡️ EDI is the automated exchange of business documents between suppliers and customers. Business processes can be optimized by exchanging information at short notice. Process cost savings and the optimization of workflows are the result.
How does the EDI process work?
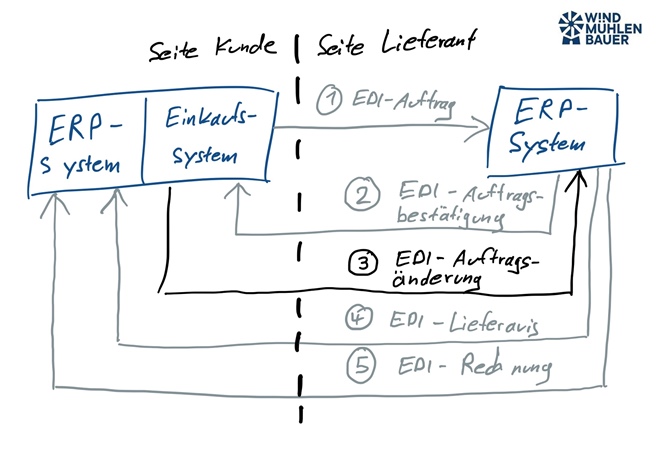
To ensure that the electronic data exchange between the partners works well, the scope must be defined. It is important to clarify which messages will be exchanged in the future and which information is mandatory. The challenge when implementing EDI processes is the purely technical perspective, the digitalization of paper-based business processes and the lack of a view of the overall process. In the perfect case, the overall process is thought through on the basis of the digital possibilities. The following illustration shows an example of the exchange of electronic business documents. We start with the order from the recipient. This is the employee who orders the items from the customer. After the exchange of further EDI messages, the process concludes with the settlement of the invoice.
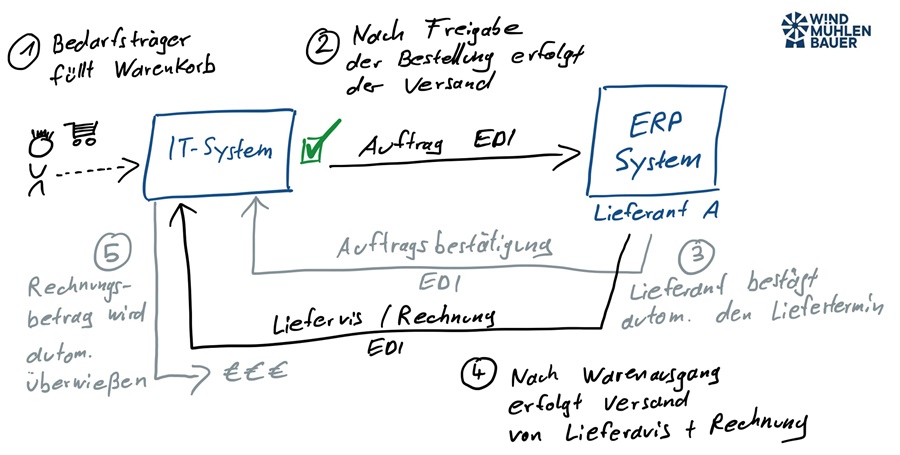
EDI standards at a glance
Over the last few years, international and industry-specific standards have been developed for the exchange of electronic data. Successful onboarding always consists of two parts. One part is the format (e.g. EDIFACT) of the EDI message. The second part is the method of transmission (e.g. AS2).
What standard EDI formats are there?
- EDIFACT: International standard for which the United Nations is responsible
- OpenTRANS: How the BMEcat was developed by the Electronic Business Standardization Committee and Fraunhofer IAO
- VDA: Is the standard of the German Association of the Automotive Industry
- IDoc: The SAP document format standard for transferring business transaction data
- X-Invoice and ZUGFerd: EDI invoices that comply with the CEN standard EN16931


What are the most common transmission routes?
- HTTPS
- AS2
- SMTP
- SFTP
What message types can be exchanged?
- Offer
- Order
- Order confirmation
- Order change
- Shipping notification
- Invoice
- Payment advice
- Credit advice
How can EDI processes be implemented?
There are basically three options for implementing EDI processes. The most convenient option is to implement the EDI messages with the help of the internal IT department. This involves translating the customer format into the format of the company’s own ERP system. Experts refer to this translation process as conversion. So-called converters can be used for this, which transfer messages into a specific format in a similar way to a translation program. A leading provider of converters is the company Seeburger.
The second option is to do this via an external service provider. In this case, your customer sends the EDI messages to an external partner, e.g. My open Factory. This partner translates the format into the format of your ERP system and imports the message (e.g. order or order change). The same applies to sending from your IT system. In this case, the service provider converts the message into a format of the customer’s choice and sends it via the agreed transmission channel.
The third and usually worst option is collaboration via webEDI. In this case, your customer processes the messages via EDI. However, it is necessary for the supplier to log into a web portal and manually transfer the information to their own IT system. Or, in the case of order confirmations and invoices, to transfer the data from their own IT system to the web portal. Further details can be found here: WEB-EDI vs. EDI > The battle for scalability.
Conclusion
Electronic data interchange, or EDI for short, helps business partners to exchange information automatically. This reduces manual data entry for both customers and suppliers. This also reduces the potential for errors and prevents incorrect deliveries and unnecessary returns. EDI is therefore ideal for optimizing business processes.
Process costs play an important role in the area of C-items. As these are low-value items (e.g. tools, safety shoes, office equipment), the cost of the ordering and delivery process should be kept as low as possible.
EDI is very well suited to reducing so-called process costs. Smooth processes and transparent information help both suppliers and customers with C-item procurement. Experience has also shown that customer loyalty increases with integrated suppliers. It is therefore a good time to increase your own EDI rate and actively approach customers!

Peter Prütting is an expert in value-oriented and digital business development. With over 15 years of sales experience from the perspectives of wholesale, manufacturing, and e-marketplaces, he takes a holistic view. His colleagues value him as a customer-centric and focused leader who guides teams through digital transformation. Away from his daily work, he recharges his batteries by mountain biking.
FAQ – Frequently asked questions
EDI stands for electronic data interchange and is made up of the first letters of the term “electronic data interchange”.
EDI (electronic data interchange) refers to the transfer of electronic data in or between IT systems. The exchange of documents or messages (e.g. orders, shipping notifications) takes place automatically without human intervention.
Company processes can be optimized through the short-term exchange of information. Process cost savings and the optimization of workflows are the result.
Sources
- EDI Factory; D96A: https://www.edifactory.de/edifact/directory/D96A/message/ORDERS
- OpenTRANS: https://www.opentrans.de/
- UNECE, EDIFACT: https://unece.org/trade/uncefact/introducing-unedifact