Imagine your products landing directly in your customers’ purchasing systems—in real time, with up-to-date prices and availability. Dynamic catalogs, also known as punchout catalogs, make this possible. They help you, as a supplier, increase sales and customer loyalty. This article provides an overview of the three most important approaches: cXML punchout, OCI catalog, and IDS Connect.
What are dynamic catalogs?
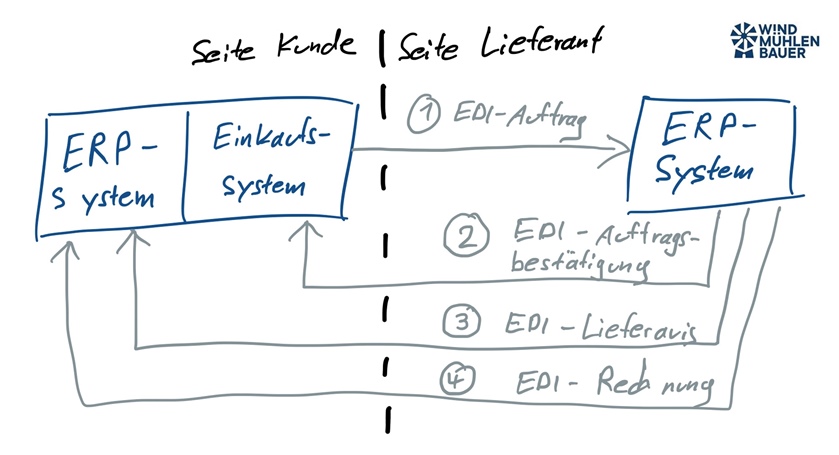
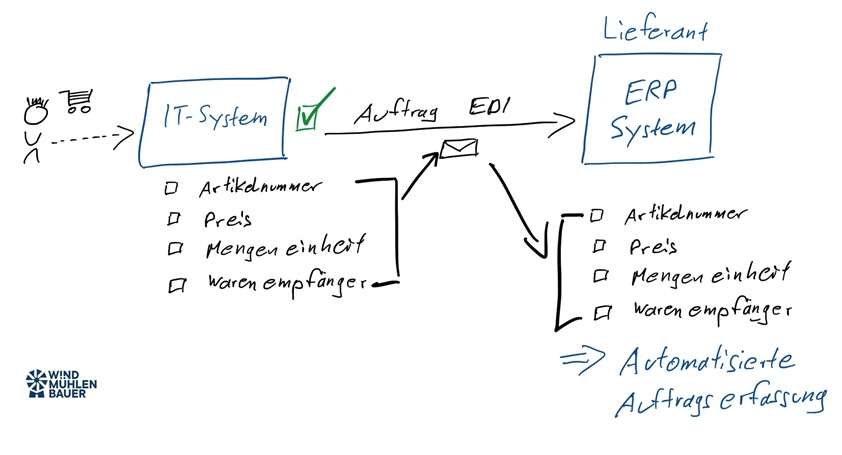
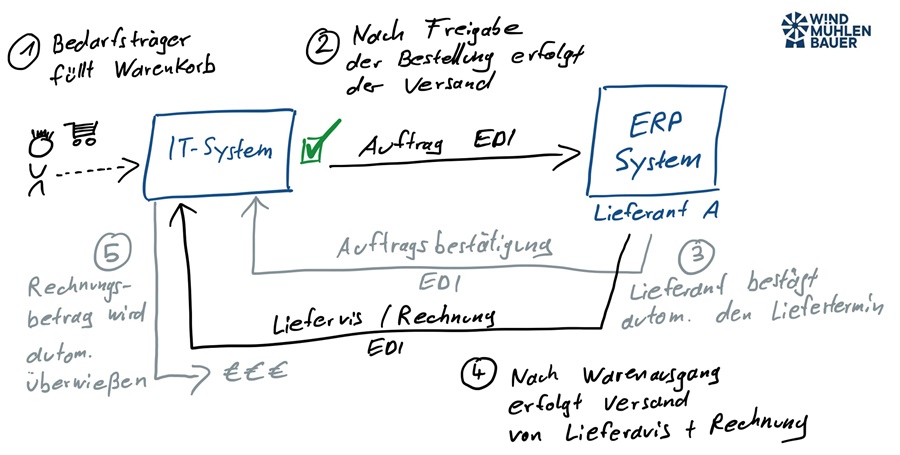
Dynamic catalogs seamlessly connect websites (e.g., web shops) with the customer’s purchasing system. Unlike static catalogs such as BMEcat or DATANORM, they update themselves in seconds without manual maintenance. Punchout catalogs can be integrated into ERP systems (e.g., SAP, HERO), e-marketplaces (e.g., simple system), or e-procurement systems (e.g., coupa, SAP Ariba). After implementation, the customer’s specialist departments are given access to the catalog. The respective employee selects the supplier and is automatically redirected to the dynamic catalog. There, the desired items are placed in the shopping cart and transferred back to the purchasing system. An order has now been created. The usual processes then take place, such as approval by the budget manager and transmission of the order to the supplier.
What are the advantages of such catalogs?
As a supplier, you benefit from the following advantages:
- You stay in control of your data: prices, stock levels, and configurations are always up to date.
- Customer uses your solution (e.g., online shop) but stays in their shopping system.
- Fewer errors, no price differences or queries
An overview of the three technical approaches
Each approach integrates external punchout catalogs into customer systems. The technology varies depending on industry standards and system landscapes.
OCI Catalog (Open Catalog Interface)
OCI, developed by SAP, is the standard for ERP and e-procurement systems such as SAP, Onventis, and Mercateo/Unite. This standard is particularly prevalent in large purchasing organizations. The goal is always to use current item data and prices for purchase orders.
cXML Punchout
cXML punchout is used in e-procurement systems such as SAP Ariba or Coupa. Its purpose is the same as that of the OCI catalog. Only the technical structure differs.
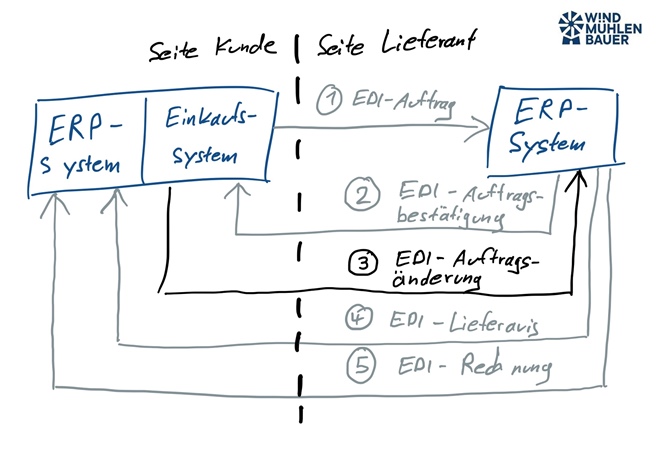
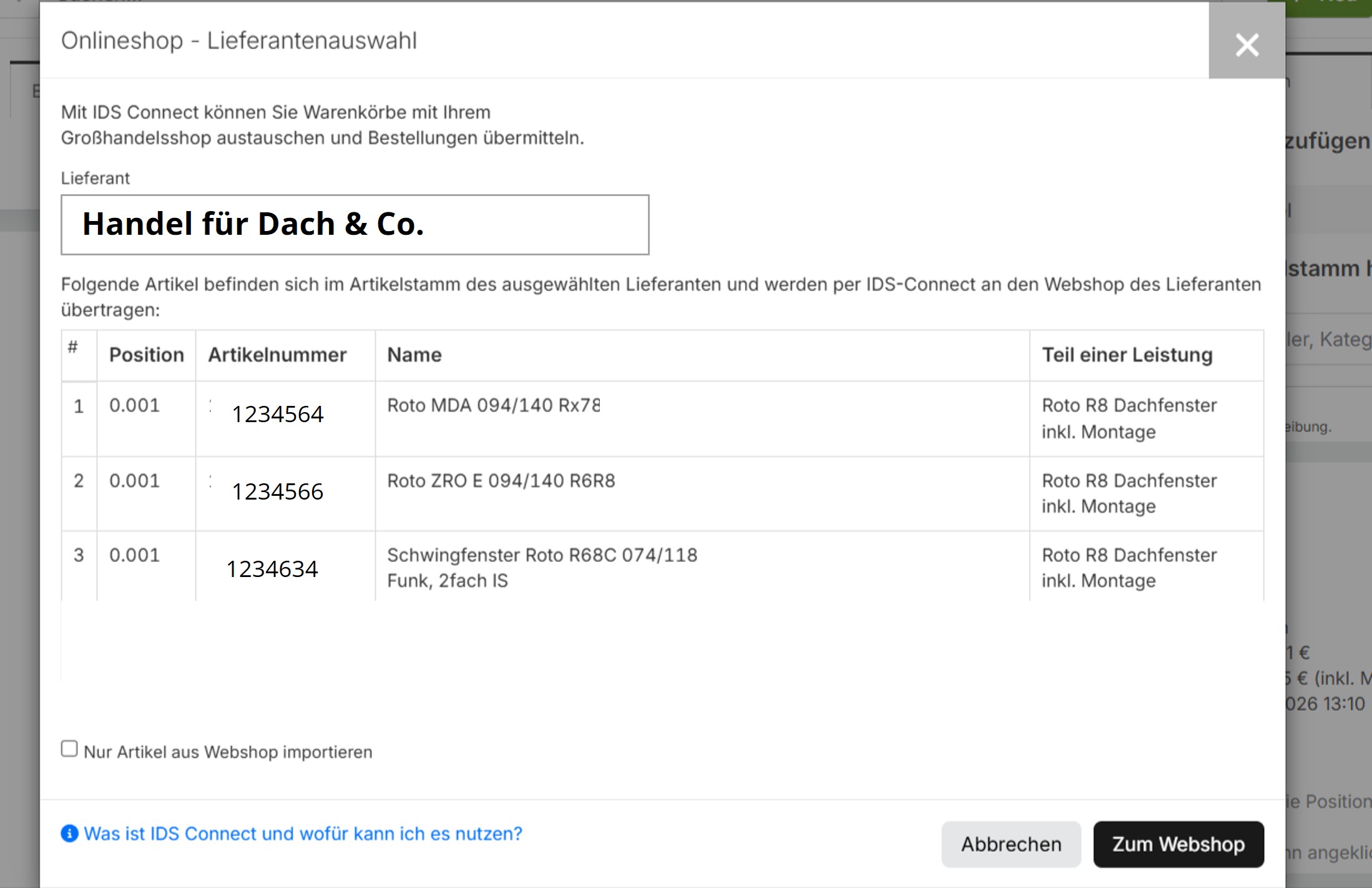
IDS Connect for craftsmen
Immer mehr Handwerksbetriebe, aus dem Branchen SHK (Sanitär-Heizung-Klima), Elektro oder Bau, setzen auf Handwerkersoftware. Diese spezialisierten ERP-Systeme haben die Standardschnittstelle IDS-Connect bereits integriert. Damit kann der Artikelstamm aktualisiert werden, Angebote geschrieben oder Bestellungen getätigt werden.
Why are punchout catalogs an important sales argument?
Does your customer use the “Preferred Supporter” label? Then you are dealing with a modern company. These customers reward suppliers who simplify the purchasing process. For example, through interfaces that help with data maintenance. That is why the ability to offer punchout catalogs is an important selling point. Because it can deliver the following benefits to the customer:
- Simplified procurement: Employees place orders in their own system without media discontinuity or manual order forms.
- Manual effort is reduced: item data and prices are transferred automatically, eliminating the need for manual order entry.
- Reduction in process costs: Transaction costs per order are falling significantly
- High data quality: Always up-to-date prices and availability
- Compliance with purchasing guidelines: Budgets and approval workflows are automatically applied and can be set across suppliers.
- Low maverick buying rate: High user-friendliness means employees use the predefined channels.
- Assortment management: Integration means that preferred suppliers are “firmly established,” allowing orders to be bundled with the “preferred supplier.”

How do I acquire the technical ability?
The classic approach involves using your own online shop and programming the required interfaces. This approach makes sense, as customer-specific prices, availability, and product data are already available in the web shop. A punchout catalog can also be implemented in other ways. The following methods are used in the market:
- In-house development: Developing the interfaces ourselves and keeping them up to date
- Plugins: Purchasing a plugin (external extension) turns the online shop into a punchout catalog. These modules are ready-made extensions for systems such as Magento, Shopware, Shopify, or Adobe Commerce.
- Out-of-the-box solution: Standard solution that generates a punchout catalog at the touch of a button using data from Excel or BMEcat. This is the cost-effective and fast solution.
Can my customer find the items using the search function in the shopping system?
Dynamic catalogs are controlled by jumping to an external website and transferring the shopping cart back. Therefore, the items cannot be found using the cross-supplier search in the ERP or purchasing system.
This disadvantage was recognized and solved with further developments in punchout techniques. With the following versions, no jump is necessary and items are displayed via the comprehensive search:
- OCI 5.0 with Background-Search
- cxML Punchout Level 2
What are the requirements for product data?
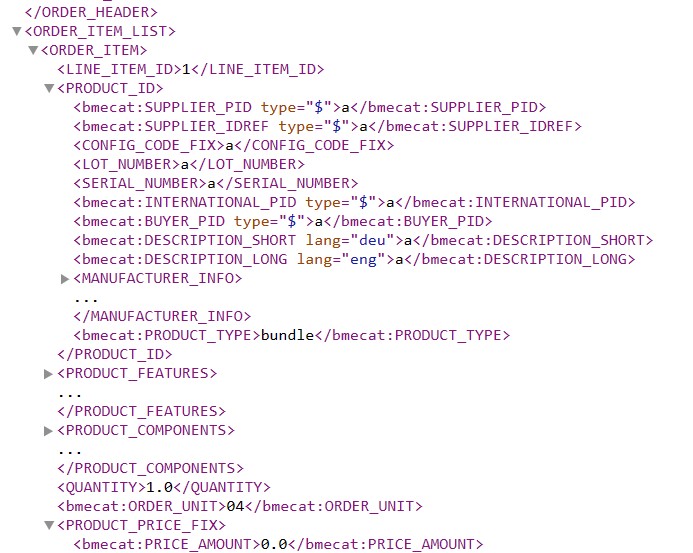
In addition to images, descriptions, documents, and customer net prices, there are two important pieces of information. These include the units of measure and the classification code.
Units of measure
Unit of measure (UOM) refers to the code that defines the unit to which the net price relates. For example, the code C62, ST, or STK can be used for the unit “piece.” These are stored for each item and must be harmonized with the customer’s logic. If the code or value is not stored with the customer, a transmission error will occur.
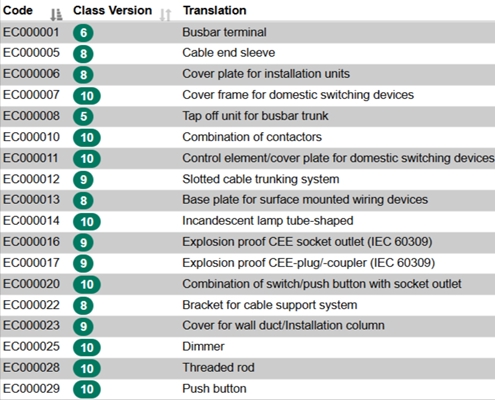
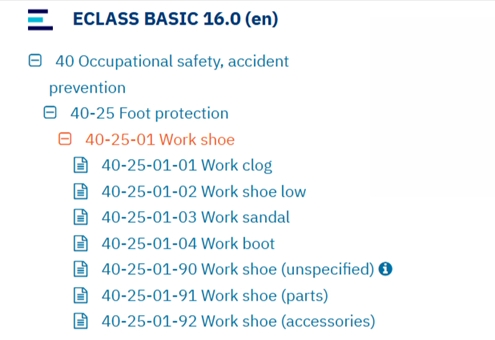
Classification Code
Classification codes are used for purchasing and financial processes. The E-Class, UNSPSC, and ETIM standards have become established. These specify the product group and partially standardize the product characteristics (e.g., ETIM). This code must be transferred for each item in the shopping cart when it is sent to the customer system.

Conclusion
Dynamic catalogs make your sales more efficient. This is because the painstakingly negotiated framework agreement is anchored in the customer’s system. This increases your visibility and allows the customer’s specialist departments to order items quickly.
That’s why it’s a good idea to invest in punchout catalogs. With modular systems that let you expand your online shop using plugins, or out-of-the-box solutions that generate a complete dynamic catalog from an Excel file at the click of a button, you can make big strides even on a small budget.
My recommendation: Start with an out-of-the-box solution. This can be set up in 2-3 hours and implemented immediately with your first pilot customer. Inform your colleagues in IT or the online shop team and sell this as a first step to conserve their resources. Your first customers will be thrilled, and you will have good arguments for implementing it in your own online shop!

Peter Prütting is an expert in value-oriented and digital business development. With over 15 years of sales experience from the perspectives of wholesale, manufacturing, and e-marketplaces, he takes a holistic view. His colleagues value him as a customer-centric and focused leader who guides teams through digital transformation. Away from his daily work, he recharges his batteries by mountain biking.
Looking for a punchout catalog?
We help you find the right solution and implement it quickly.
FAQ – Frequently asked questions
A dynamic catalog (also known as a punchout catalog) connects your online store directly to your customer’s purchasing system. Prices, availability, and product data are automatically transferred in real time. This allows your customer to access, select, and order your products directly in their system—without having to enter any data manually.
A static catalog (e.g., DATANORM, BMEcat) must be updated manually on a regular basis. A dynamic catalog, on the other hand, updates itself automatically via an interface. Changes to prices or items are visible immediately, saving time and avoiding errors.
Your data remains up to date and under your control. Customers can see your prices and stock levels directly. Order processes run faster and without errors. You retain your customers in the long term, which increases your chances of follow-up orders.
Different standards are used depending on the customer system:
➡️ IDS Connect: mainly used in craftsman ERP systems such as HERO.
➡️ OCI catalog (Open Catalog Interface): standard for SAP, Onventis, or Mercateo.
➡️ cXML punchout: frequently used for large platforms such as SAP Ariba or Coupa.
There are three ways: #1 In-house development: You program the interface yourself. #2 Plugin: You purchase an extension (e.g., for Shopware, Magento, Shopify). #3 Standard solution: You use a ready-made “out-of-the-box” version—ideal for a quick start.
Complete product information is important. In addition, the units of measurement must be coordinated. Most customers also require classification codes according to E-Class, UNSPSC, or ETIM standards. This information is crucial for ensuring that data exchange with the customer’s system runs smoothly.
This was not possible in older versions, as the process involved jumping to an external website where the shopping cart was sent to the original system. Newer versions such as OCI 5.0 or cXML Punchout Level 2 offer an integrated search function, meaning that your items appear directly in the search results of the customer’s system.
Because your products are right where customers shop. No unnecessary searching or detours via websites are necessary. This increases convenience and trust and leads to additional sales.
Sources
- WMB Magazine, How does a punchout catalog work?: https://windmuehlenbauer.com/punchout-katalog/
- WMB Magazine, Open Catalog Interface – The smart way into the customer system. https://windmuehlenbauer.com/open-catalog-interface/
- WMB Magazine, What is a cXML punchout catalog?: https://windmuehlenbauer.com/cxml-punchout-catalog/
- WMB Magazine, IDS Connect: Increased efficiency for tradespeople: https://windmuehlenbauer.com/ids-connect/
- Classification, UNSPSC: https://www.ungm.org/public/unspsc
- Classification, E-Class: https://eclass.eu/eclass-standard/content-suche
- Classification, ETIM: https://prod.etim-international.com/class